上海金畔生物科技有限公司为生命科学和医药研发人员提供生物活性分子抑制剂、激动剂、特异性抑制剂、化合物库、重组蛋白,专注于信号通路和疾病研究领域。
Oxaliplatin (Synonyms: 奥沙利铂) 纯度: ≥98.0%
Oxaliplatin 是一种 DNA 合成 抑制剂。Oxaliplatin 会导致 DNA 交联损伤,阻止 DNA 复制和转录并导致细胞死亡。Oxaliplatin 以时间依赖方式抑制人黑色素瘤细胞系 C32 和 G361,IC50 值分别为 0.98 μM 和 0.14 μM。Oxaliplatin 可以诱导细胞自噬 (autophagy)。
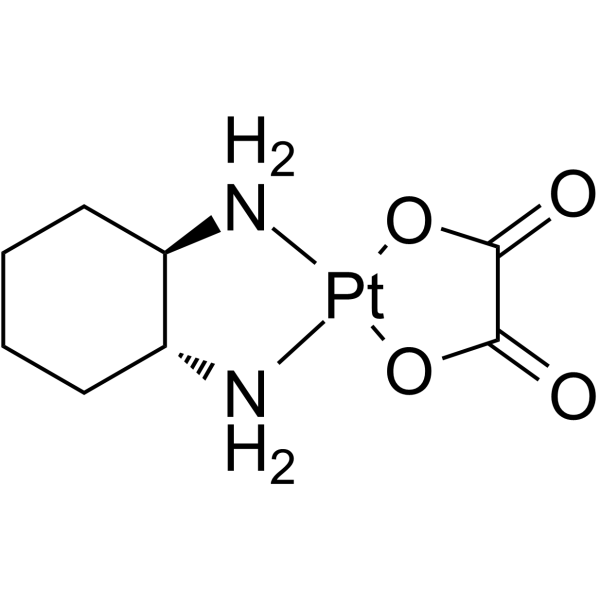
Oxaliplatin Chemical Structure
CAS No. : 61825-94-3
| 规格 | 价格 | 是否有货 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free Sample (0.1-0.5 mg) | Apply now | ||
| 5 mg | ¥450 | In-stock | |
| 50 mg | ¥550 | In-stock | |
| 100 mg | ¥818 | In-stock | |
| 200 mg | ¥1400 | In-stock | |
| 500 mg | ¥3200 | In-stock | |
| 1 g | 询价 | ||
| 5 g | 询价 |
* Please select Quantity before adding items.
Oxaliplatin 相关产品
•相关化合物库:
- Drug Repurposing Compound Library Plus
- FDA-Approved Drug Library Plus
- Bioactive Compound Library Plus
- Cell Cycle/DNA Damage Compound Library
- FDA-Approved Drug Library
- Anti-Cancer Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Drug Repurposing Compound Library
- NMPA-Approved Drug Library
- FDA Approved & Pharmacopeial Drug Library
- Anti-Lung Cancer Compound Library
- Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Compound Library
- Anti-Blood Cancer Compound Library
- Rare Diseases Drug Library
- Children’s Drug Library
| 生物活性 |
Oxaliplatin is a DNA synthesis inhibitor. Oxaliplatin causes DNA crosslinking damage, prevents DNA replication and transcription and causes cell death. Oxaliplatin time-dependently inhibits human melanoma cell lines C32 and G361 with IC50 values of 0.98 μM and 0.14 μM, respectively. Oxaliplatin induces cell autophagy[1][2]. |
IC50 & Target |
IC50: DNA synthesis[1] |
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Oxaliplatin acts through the formation of DNA-adducts. Oxaliplatin induces primary and secondary DNA lesions leading to cell apoptosis[1]. Oxaliplatin inhibits human melanoma cell lines C32 and G361 with IC50 values of 0.98 μM and 0.14 μM, respectively[2]. Oxaliplatin potently inhibits bladder carcinoma cell lines RT4 and TCCSUP, ovarian carcinoma cell line A2780, colon carcinoma cell line HT-29, glioblastoma cell lines U-373MG and U-87MG, and melanoma cell lines SK-MEL-2 and HT-144 with IC50 of 11 μM, 15 μM, 0.17 μM, 0.97 μM, 2.95 μM, 17.6 μM, 30.9 μM and 7.85 μM, respectively[3].For storage 5% Glucose can be used as a in vitro preparing solution[1]. You can prepare a 5 mM (2 mg/mL) Oxaliplatin solution (or you can refer to the solubility data on datasheet), chemical and physical in-use stability has been demonstrated for up to 48 hours at 2°C-8°C, 7 days at -20°C. 上海金畔生物科技有限公司 has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
||||||||||||||||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Oxaliplatin (10 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly reduces tumor volume and apoptotic index in the nude mice bearing hepatocellular HCCLM3 tumors[4]. Oxaliplatin (5 mg/kg, i.v.) is effective on T-leukemia-lymphoma L40 AKR with T/C of 1.77. Oxaliplatin is efficient on intracerebrally grafted L1210 leukemia, MA 16-C xenografts, B16 melanoma xenografts, Lewis lung xenografts and C26 colon carcinoma xenografts[5]. Oxaliplatin induces impairment of retrograde neuronal transport in mice[6]. 上海金畔生物科技有限公司 has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
||||||||||||||||
| Clinical Trial |
|
||||||||||||||||
| 分子量 |
397.29 |
||||||||||||||||
| Formula |
C8H14N2O4Pt |
||||||||||||||||
| CAS 号 |
61825-94-3 |
||||||||||||||||
| 中文名称 |
奥沙利铂 |
||||||||||||||||
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature in continental US; may vary elsewhere. |
||||||||||||||||
| 储存方式 |
4°C, protect from light *In solvent : -80°C, 6 months; -20°C, 1 month (protect from light) |
||||||||||||||||
| 溶解性数据 |
In Vitro:
H2O : 2.17 mg/mL (5.46 mM; ultrasonic and warming and heat to 60°C; DMSO can inactivate Oxaliplatin’s activity) DMF : 1.67 mg/mL (4.20 mM; Need ultrasonic; DMSO can inactivate Oxaliplatin’s activity) Ethanol : < 1 mg/mL (insoluble; DMSO can inactivate Oxaliplatin’s activity) 配制储备液
*
请根据产品在不同溶剂中的溶解度选择合适的溶剂配制储备液;一旦配成溶液,请分装保存,避免反复冻融造成的产品失效。 In Vivo:
请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解方案。以下溶解方案都请先按照 In Vitro 方式配制澄清的储备液,再依次添加助溶剂: ——为保证实验结果的可靠性,澄清的储备液可以根据储存条件,适当保存;体内实验的工作液,建议您现用现配,当天使用; 以下溶剂前显示的百
*以上所有助溶剂都可在 上海金畔生物科技有限公司 网站选购。
|
||||||||||||||||
| 参考文献 |
|
| Cell Assay [3] |
Typically, cells are plated into 96-well plates on day 0 and exposed to Oxaliplatin on day 1; the sulforhodamine-B assay is carried out 48 h after Oxaliplatin exposure. The plates are incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 and 100% relative humidity at all times except when adding Oxaliplatin and during the final assay period. The initial number of cells plated for the assay ranged from 2-20×103 cells/50/nL/well. The numbers of cells for plating and the drug exposure time are based on pilot studies using the criteria that (a) the cells in control wells are still in the log phase of growth on the day of the assay; (b) the maximum absorbance for the untreated controls on the day of the assay is in the range of 1.0 to 1.5; and (c) cells go through > 2 doublings during the drug exposure. Eight wells are used per concentration. The plates are read at 570 and/or 540 nm using a Biotek Instruments model EL309 microplate reader interfaced with an IBM PC-compatible computer. 上海金畔生物科技有限公司 has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
|---|---|
| Animal Administration [4] |
HCC tumor models produced by HCCLM3 are established in nude mice by subcutaneous injection of 5×105 HCCLM3 cells in 0.2 mL of serum-free culture medium into the left upper flank region. Three days later, the mice are randomLy assigned to receive one of the following three treatments: i) a weekly intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of distilled water (control group, n=8); ii) a weekly i.p. injection of oxaliplatin at 5 mg/kg (low dose group, n=7); or iii) a weekly i.p. injection of oxaliplatin at 10 mg/kg (high dose group, n=7). Tumor growth is monitored by measuring two bisecting diameters of each tumor with a caliper every 5 days. The tumor volume is calculated using the formula (V=a×b2/2), with a as the larger diameter and b as the smaller diameter. Mice are euthanized by day 32 after oxaliplatin administration. Tumors of each group are completely removed, weighed, photographed, and fixed in 10% formalin/PBS or stored in liquid nitrogen for histological examination. 上海金畔生物科技有限公司 has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
| 参考文献 |
|
所有产品仅用作科学研究或药证申报,我们不为任何个人用途提供产品和服务
