Colchicine (Synonyms: 秋水仙碱) 纯度: 99.87%
Colchicine 是微管蛋白 (tubulin) 抑制剂和微管 (microtubule) 干扰剂。 Colchicine 抑制微管聚合的 IC50 为 3 nM。Colchicine 还是 α3 甘氨酸受体 (GlyRs) 的竞争性拮抗剂。
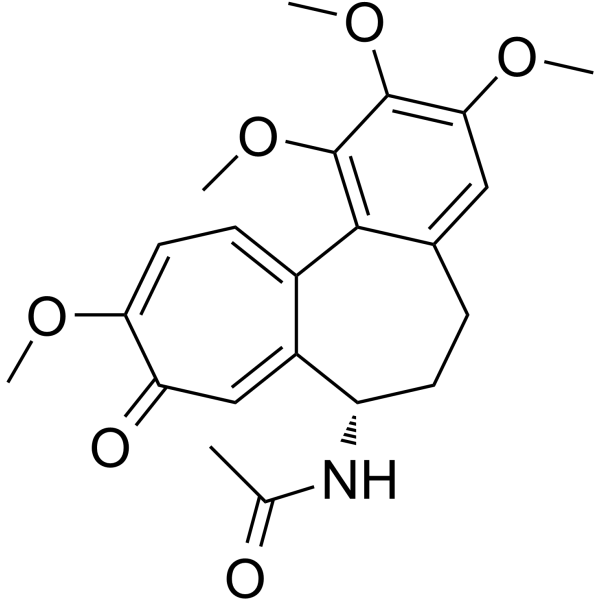
Colchicine Chemical Structure
CAS No. : 64-86-8
| 规格 | 价格 | 是否有货 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free Sample (0.1-0.5 mg) | Apply now | ||
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO | ¥500 | In-stock | |
| 200 mg | ¥350 | In-stock | |
| 500 mg | ¥650 | In-stock | |
| 1 g | 询价 | ||
| 5 g | 询价 |
* Please select Quantity before adding items.
Colchicine 相关产品
•相关化合物库:
- Natural Product Library Plus
- Drug Repurposing Compound Library Plus
- FDA-Approved Drug Library Plus
- FDA-Approved Drug Library Mini
- Bioactive Compound Library Plus
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Cell Cycle/DNA Damage Compound Library
- Natural Product Library
- FDA-Approved Drug Library
- Anti-Cancer Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Drug Repurposing Compound Library
- NMPA-Approved Drug Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Cytoskeleton Compound Library
- Orally Active Compound Library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Monomer Library
- FDA Approved & Pharmacopeial Drug Library
- Alkaloids Library
- Anti-Lung Cancer Compound Library
- Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Compound Library
- Rare Diseases Drug Library
- Children’s Drug Library
| 生物活性 |
Colchicine is a tubulin inhibitor and a microtubule disrupting agent. Colchicine inhibits microtubule polymerization with an IC50 of 3 nM[1][2][3]. Colchicine is also a competitive antagonist of the α3 glycine receptors (GlyRs)[4]. |
IC50 & Target |
Microtubule/Tubulin[1] |
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Exposure to 1μM Colchicine, a microtubule disrupting agent, triggered apoptosis in rat cerebellar granule cells (CGC). Colchicine treatment also causes alterations in Ca2+ responses to chemical depolarization and a moderate, but progressive, increase in the resting intracellular Ca2+ concentration[1]. Colchicine exerts its biological effects through binding to the soluble tubulin heterodimer, the major component of the microtubule. The Colchicine binding abilities of tubulins from a variety of sources are summarized, and the mechanism of Colchicine binding to brain tubulin is explored in depth. The relationship between colchicinoid structure and tubulin binding activity provides insight into the structural features of Colchicine responsible for high affinity binding to tubulin and is reviewed for analogs in the Colchicine series. The thermodynamic and kinetic aspects of the association are described and evaluated in terms of the binding mechanism. Colchicine binding to tubulin results in unusual alterations in the low energy electronic spectra of Colchicine. The spectroscopic features of Colchicine bound to tubulin are discussed in terms of the nature of the Colchicine-tubulin complex. Attempts to locate the high affinity Colchicine binding site on tubulin are presented[2]. Colchicine treatment inhibits indomethacin-induced small intestinal injury by 86% (1 mg/kg) and 94% (3 mg/kg) as indicated by the lesion index 24 h after indomethacin administration. Colchicine inhibits the protein expression of cleaved caspase-1 and mature IL-1β, without affecting the mRNA expression of NLRP3 and IL-1β[3]. MCE has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
||||||||||||||||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Vehicle or Colchicine (1 mg/kg) is administered orally 30 min prior to indomethacin administration. The lesions stained with Evans blue in the small intestine are smaller in Colchicine-treated mice than those in vehicle-treated mice 24 h after indomethacin administration. In addition, histological examination shows that Colchicine-treated mice have less mucosal inflammation and ulceration and a decrease in the size and numbers of lesions compared with vehicle-treated mice. Colchicine treatment significantly reduces the lesion index at doses of 1 mg/kg and 3 mg/kg (by 86% and 94%, respectively) compared with vehicle treatment. Colchicine treatment significantly inhibits the protein levels of mature IL-1β at doses of 1 mg/kg and 3 mg/kg (by 56% and 69%, respectively) without affecting those of pro-IL-1β. Colchicine treatment also significantly inhibits the protein levels of cleaved caspase-1 at doses of 1 mg/kg and 3 mg/kg (by 26% and 39%, respectively) without affecting those of pro-caspase-1[3]. MCE has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
||||||||||||||||
| Clinical Trial |
|
||||||||||||||||
| 分子量 |
399.44 |
||||||||||||||||
| Formula |
C22H25NO6 |
||||||||||||||||
| CAS 号 |
64-86-8 |
||||||||||||||||
| 中文名称 |
秋水仙素;秋水仙碱 |
||||||||||||||||
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature in continental US; may vary elsewhere. |
||||||||||||||||
| 储存方式 |
|
||||||||||||||||
| 溶解性数据 |
In Vitro:
DMSO : ≥ 48 mg/mL (120.17 mM) H2O : ≥ 33.33 mg/mL (83.44 mM) * “≥” means soluble, but saturation unknown. 配制储备液
*
请根据产品在不同溶剂中的溶解度选择合适的溶剂配制储备液;一旦配成溶液,请分装保存,避免反复冻融造成的产品失效。 In Vivo:
请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解方案。以下溶解方案都请先按照 In Vitro 方式配制澄清的储备液,再依次添加助溶剂: ——为保证实验结果的可靠性,澄清的储备液可以根据储存条件,适当保存;体内实验的工作液,建议您现用现配,当天使用; 以下溶剂前显示的百
*以上所有助溶剂都可在 MCE 网站选购。
|
||||||||||||||||
| 参考文献 |
|
| Animal Administration [3] |
Mice[3] MCE has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
|---|---|
| 参考文献 |
|
